We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience, serve personalized ads or content, and analyze our traffic. By clicking "Accept All", you consent to our use of cookies.
Cookie preferences
| Cookie | Provider | Purpose | Expiry |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHP_SESSID | texfire.net | The PHPSESSID cookie is native to PHP and allows websites to store serialised status data. On the website it is used to establish a user session and to pass state data through a temporary cookie, which is commonly known as a session cookie. These Cookies will only remain on your computer until you close your browser. | Session |
| PrestaShop-# | texfire.net | This is a cookie used by Prestashop to store information and keep the user's session open. It stores information such as currency, language, customer ID, among other data necessary for the proper functioning of the shop. | 480 hours |
- HOME
- +Flame retardant fabrics
- Mineral Fiber Fabrics
- Aluminized fabric
- Coatings
- Multilayered fabric
- Nonwoven
- Welding fabric
- Thermal barrier fabric
- Thermal shield fabric
- Fabric for extreme temperatures
- Fabric for foundries
- Fabric for electric companies
- Fabric for petrochemistry
- Fabric for events and pyrotechnics
- Aramid Fabrics
- Fabrics for Mechanical Strain
- Emergency Services Fabrics
- +Flame retardant products
- +Textile lagging
- Company
- Technical videos
- Trabaja con nosotros
UNE-EN ISO 11611:2018 Protective clothing for use in welding and allied processes
Application range
This regulation especifies the minimun requirements and test methods to extintion clothing, including hoods, aprons, sleeves and spats used for users' protection during the welding operations and affine processes. This type of protection clothes are used to protect a user from small cast metal spashes, small contact periodes with fite, radiant heat produced by the welding arc and minize the chance of an electrical shoc by the accidental contact with electrical conductors with a 100 V d.c. voltage.
The regulation sets two level of protection:
- Class 1: Protection against lower damages in welding jobs and situations that provoke lower levels of splashes and radiant heat.
- Class 2: Protection against higher damages in welding jobs and situantions that provoke higher levels of spashes and radiant heat.
General Requisites
ISO 13688
Sizes: according to ISO 13688.
Design: Protection clothes for welding jobs must be designed without any electric conductions from the outside to the inside of the clothes, this will be ensured visually.
When the piece is composed by different clothing (jacket and trousers), the jacket must have enough length to overlap with the higher part of the trousers from at leats 20 cm. This minimum overlapping must be kept in all positions and movements expected during its use.
Pockets: if necessary, must be created with materials following EN 15025 regulations (fire propagation). External pockets in jackets and trousers, except lateral pockets under waist that doesn't make a superior angle to 10º with lateral sewing, must be covered by labels 20mm wider than the pockets averture at least.
Closures must be designed with a protection label outside the suit. Buttonholes' maximum distance must be 150 mm. Zippers must stop when are completely closed. Cuffs could have closures to reduce their width. Neck's apperture must be provided of a closure. Jackets and coveralls' sleeves, as well as the bottom of the trousers, will not have any hem.
Additional clothing (hoods, hoses, aprons and gaiters): must be designed to offer extra protection in specific areas of the body, always wearing them with the main protection suit.
Preprocessing
ISO 6330 / ISO 15797
Before each test clothes must be cleaned according to manufacturer's conditions. Additionally, during the limited fire propagation fire test will be done before and after the wash. Leather will not have preprocessing. If not specified, there will be a minimum ammount of 5 washes.
Termic features
ISO 15025
Limited fire propagation: Materials and seams must be tested under A procedure (A1 code) or B procedure (A2 code). When testing with A procedure, the following requisistes must be accomplished:
- Any sample must burn until superior or lateral edges
- A hole must not be caused in any sample
- Any burnt or melted rest must be released in any sample
- Afterburner average time must be 2s
- Residual incandescence average time must be 2s
When seams are tested, they must remain unchanged
When testing with B procedure, samples with hem must meet the following requisites:
- Any sample must burn until superior or lateral edges
- Any burnt or melted rest must be released by any sample
- Afterburner average time must be 2s
- Residual incandescence average time must be 2s
When seams are tested, with hem, they must remained unchanged.
ISO 9150
Small splashes impact: According to the ammount of metal drops that the fabric holds before calorimeter's temperature raises from 40ºK, fabrics must be classified as:
- Class 1 > 15 drops
- Class 2 > 25 drops
ISO 6942
Calor radiante: realizando el ensayo con una densidad de flujo calorífico de 20 kW/m2 , el índice de transferencia de calor radiante (RHTI 24 ºC) debe ser:
- Para Clase 1: RHTI 24 7
- Para Clase 2: RHTI 24 16
EN 1149-2
Electric resistance: before testing, samples must be conditioned to a 20 ºC ± 2 ºC temperature and a relative humidity of 85% ± 5% . Applying an electrical potential of 100 V ± 5 V, electric resistance must be higher than 105 , for all clothing's layers.
Mechanical features
ISO 5077
Dimensional variations: Textile materials of the fabric, non-woven fabrics and laminated fabrics, must not be superior to 3%. Dimensional variation of knitted fabrics must not be superior to 5%.
ISO 13934-1
Traction resistance: traction resistance of external materials, except leather and knitted materials, must be 400N minimum in both directions (warp and woof). For leather and tested according EN 3376, traction resistance must be at least 80 N in both directions.
ISO 13937-2
Ripping resistance: Ripping resistance of external material and leather must be at least 20 N in both directions. For leather fabrics, ripping resistance must be tested according to ISO 3377-1 regulations.
ISO 13938-1
Ripping resistance: Ripping resistance of external material and leather must be at least 20 N in both directions. For leather fabrics, ripping resistance must be tested according to ISO 3377-1 regulations.
ISO 13935-2
Seams resistance: the material or the ensemble external clothing must show at least a resistance of 225 N in fabrics and 110N in leather.
EN 343
Optional requisite. Requisito opcional. Water penetration resistance (W code): if a water penetration feature is needed, clothing must be tested and clasified for water penetration and steam resistance, meeting the following requisites:
- Water penetration resistance must be tested and clasified according to EN 343 regulations.
- Steam penetration resistance must be tested and clasified according to EN 343 regulations.
ISO 13688
MARKING: Pictogram

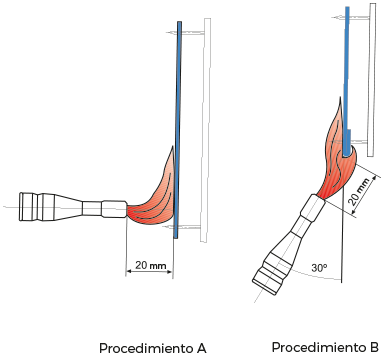
A procedure: Superficial ignition, lighter is set perpendiculary to the fabrics's surface. Flame is applied during 10 s and the following information is observed and registered:
- If flame reaches superior edge or any edge of the sample
- Burning time
- After incandescent time
- If after incandescence is extended beyond burnt area
- Residual detachment
- If residues burn filter paperIf a whole is made and in what layed is caused
B procedure: Edge ignition, lighter is set forming a 30º angle from vertical. Distance between lighter's edge and fabric's inferior edge must be 20 mm ± 2 mm. Flame is applied during 10 s and the preceeding information, except section g), is observed and registered.